With more and more applications of insulated glass, the sealing life, which is as important as energy-saving of insulated glass, has not been given enough attention, and the energy-saving effect and sealing life of insulated glass with different structures vary greatly. Insulated glass with poor sealing life not only affects the visibility of the glass itself, but also the energy-saving effect of the insulated glass. The factors influencing the sealing life of insulated glass are: sealant, sealing structure, spacer strip (e.g. warm edge technology), desiccant, working quality and quality control.
Factors Affecting Sealing Life of Insulated Glass
1. The material used to make insulated glass directly affects the sealing life of insulated glass, so raw materials meeting production requirements should be selected, including: original glass, aluminium strips and inserts, molecular sieve (desiccant), sealant (butyl rubber, polysulfide, silicone gel, etc.).
2. Good structural design also affects the sealing life of insulated glass, so it is better to use energy-saving and better sealing two-way sealing structure.
3. When the material and structure meet the requirements, we also need to pay attention to the production process of insulated glass, control the quality of each link in the production process and ensure the production of qualified products.
Meaning of Failure of Insulated Glass Seal
When insulating glass is used, the seal failure can be determined if the following conditions occur: condensation (frost) in the hollow cavity, the insulated glass does not flex under the conditions of wind pressure, climate and air pressure changes, and the initial dew point of the insulating glass changes through the climate temperature and humidity Significant changes occurred afterwards, and the volume of argon in the insulated glass air layer decreased. People can test the sealing performance of insulating glass through experimental methods:
1. Initial dew point and frost point can not pass through. This means that the residual water in the cavity of insulated glass reaches saturation at -40℃. If the initial dew point of the insulated glass is also reached at higher temperatures, it is highly possible that the sealing structure of the insulated glass has cracked. This happens mostly on insulated glass made of composite adhesive strips.
2. Vacuum tank test failed. Indicates that the seal of the insulated glass has clearance so that the insulated glass does not flex outwards in vacuum. This phenomenon mostly occurs in the case of poor labor quality.
3. The ultraviolet radiation failed, and the oil film formed after cooling appeared on the inner glass wall in the insulated glass air layer. It means that the desiccant in the insulated glass cannot effectively absorb the volatile organic solvent in the air layer. This situation is likely to occur on insulated glass made of polysulfide glue single-pass seal and 3A or 4A molecular sieve desiccant.
4. High temperature and humidity test failed.It indicates that there is condensation in the air layer of the insulated glass, which is caused by the fact that the insulated glass adhesive sealant can not effectively prevent foreign water from entering the insulated glass. This can easily occur on insulated glass with polysulfide single-pass seals.
5. The climate cycle test failed. It means that there is water condensation in the air layer of the insulating glass. The cause is that the insulating glass sealant does not effectively prevent external moisture from entering the insulating glass. This situation mostly occurs in insulated glass made of composite rubber strips.
6. Argon retention rate test shows a significant change before and after retention rate test. This indicates that a gap in the seal of the insulated glass results in an increase in the dew point after the test.
7.P1 test is an accelerated aging test for testing sealing life of insulated glass.Test conditions: high temperature 600℃, continuous sprinkler and 2500uw/c㎡ ultraviolet radiation. The seal life of different insulated glass(sealed) structures differs considerably.
Super Spacer
Insulated glass spacers play a unique role in insulated glass structure, sealing life and energy saving.Unlike other configuration elements of insulated glass, spacer bars are the only materials that can affect energy saving and sealing life of insulated glass.
From the energy-saving point of view of insulated glass, insulated glass goes through three different stages: metal spacer strip, comfort strip and super spacer. Super spacer have the best energy-saving performance, followed by comfortable rubber strips and metal spacer strips. Super spacer is a new generation of insulated glass spacer strip appearing in 1987, which is characterized by energy saving and long sealing life of insulated glass.
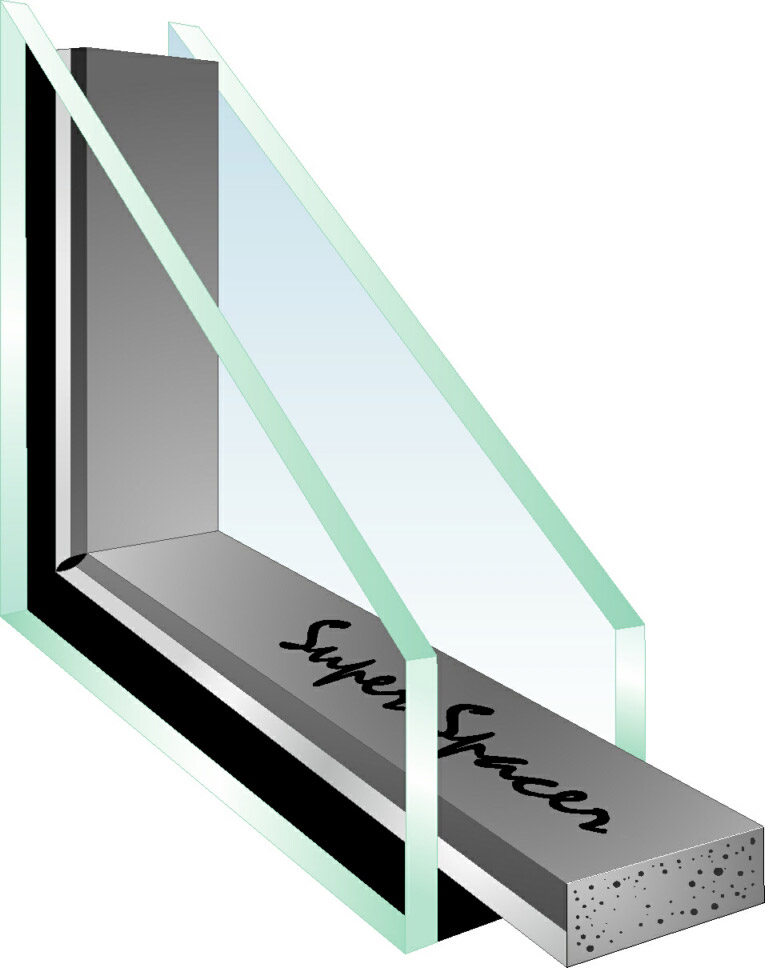
Single seal, double seal and reactive hot melt adhesive
Sealants play an important role in the sealing life of insulated glass.
1. The two-way seal structure is better than the single-way seal structure, but the single-way seal has the advantages of less process investment, convenient and low processing cost.
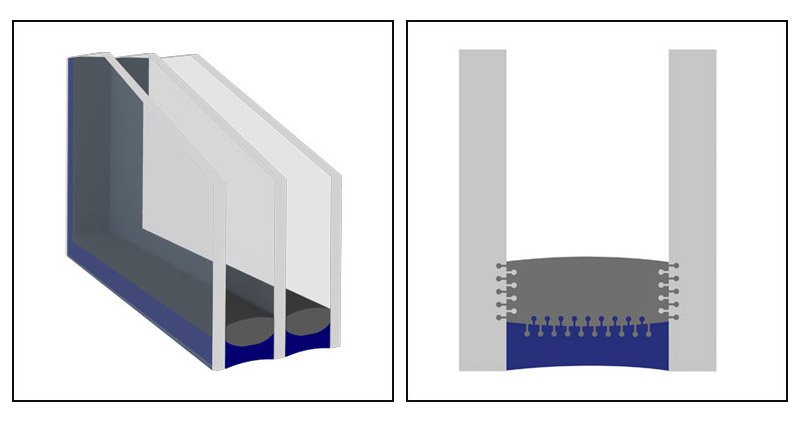
2. Because the energy saving of insulating glass is not affected by the structure of insulating glass, reactive hot melt adhesives, which have the advantages of double sealing and single sealing at the same time, appeared in 1997-1998. The working principle is that the hot melt glue itself is used as the base glue, and the water vapor in the environment and the colloidal substrate is used as the catalyst (curing agent), and it reacts immediately after contact. The advantages are low water vapor permeability, strong structure, convenient processing, less site area, and lower cost. Since the reactive hot melt adhesive provides the structural and sealing properties required for insulating glass at the same time, more and more people use it to replace the traditional double-channel sealing structure. This kind of reactive hot melt adhesive is also referred to as DSE for short, which is equivalent to a single-channel sealing structural adhesive for double-channel sealing. According to relevant data, the sealing life of using reactive hot melt adhesive can reach more than 60 years.

To judge whether the insulating glass technology is advanced, it is necessary to determine whether it can meet the dual purpose of energy saving and long sealing life. To improve the energy-saving effect of insulating glass, low-radiation glass can be used to replace white float glass, and air can be replaced with inert gas. Similarly, extending the sealing life of insulating glass can also be achieved by rationally selecting sealants, desiccants and sealing structures.